Summary
- Lower your small business tax bill by identifying deductible expenses that reduce taxable income.
- Common expenses that can be deducted include rent, utilities, salaries, and office supplies.
- Expenses must be both ordinary and necessary for your business to qualify for a deduction.
- Misunderstanding deductions can lead to lost savings or trouble with the IRS.
- Accurate expense tracking is crucial to maximizing deductions and ensuring compliance.
Understanding Deductible Small Business Expenses
Running a small business is a big job. One of the smartest things you can do is identify deductible expenses that can lower your taxable income. This means you pay less in taxes, leaving more money in your pocket to invest back into your business. The IRS allows businesses to deduct certain expenses, but it’s important to know which ones qualify.

Consider deductible expenses as tools in your financial toolbox. They assist you in managing your finances more efficiently, giving you more control over the success of your business. By comprehending these deductions, you can save money and avoid possible problems with tax authorities.
Why Identifying Deductible Expenses is Crucial
Recognizing deductible expenses isn’t just about cutting costs—it’s about enhancing your company’s financial well-being. When you accurately identify and claim these expenses, you’re effectively giving your business a financial leg up. Every dollar you save on taxes is a dollar you can put back into your business, whether that’s for new equipment, hiring employees, or advertising campaigns.
Furthermore, understanding these deductions helps you stay in line with tax laws. The IRS requires businesses to keep accurate records, and knowing which expenses are deductible ensures you keep the right documentation. This reduces the risk of audits and penalties, giving you peace of mind. For more insights, check out these small business tax planning tips.
- Maximize savings by reducing taxable income.
- Reinvest savings into business growth.
- Ensure compliance with tax laws and reduce audit risks.
Basic Criteria for Tax Deductibility
To determine if an expense is deductible, it must meet two basic criteria: it must be ordinary and necessary. An ordinary expense is one that is common and accepted in your industry. For example, purchasing office supplies is ordinary for most businesses. A necessary expense is one that is helpful and appropriate for your business. This doesn’t mean it has to be indispensable, but it should be relevant to your operations.
Popular Misunderstandings
There are a number of misunderstandings among small business owners about what counts as a deductible expense. One widespread misunderstanding is that all expenses related to the business are deductible. This is not the case. Only expenses that meet the criteria set out by the IRS are deductible. Also, some think that personal expenses used for business can be fully deducted. In fact, only the business portion of these expenses can be claimed.
Many people also believe that claiming a large number of deductions will result in an audit. Although it is true that claiming an excessive number of deductions or deductions that are out of the ordinary may raise some eyebrows, there is no reason to be concerned as long as you have the necessary documentation and the expenses are legitimate.
Categories of Deductible Small Business Expenses
It’s crucial to comprehend the various categories of deductible expenses in order to optimize your tax savings. Operating expenses, capital expenses, inventory costs, and home office expenses are all broad categories of these expenses. Each category has its own set of regulations and guidelines, so it’s crucial to become familiar with them. For more insights, explore our small business tax planning tips.
Day-to-Day Business Costs
Day-to-day business costs are the expenses you face in the normal operation of your business. These can include rent, utilities, office supplies, salaries, and insurance. Most of these costs can be fully deducted in the year they occur. They are vital for maintaining your business operations.
For example, if you lease a workspace, the lease payments are classified as operating costs. Likewise, utilities like power, water, and internet that are used for business operations can be deducted. It’s crucial to keep meticulous records of these expenses to ensure they’re correctly reported on your tax forms. For more information, consider reviewing the business expense categories that are tax-deductible.
Capital Expenses
Capital expenses are the costs you incur when you buy assets that will be useful for more than the current tax year. Examples of capital expenses include equipment, vehicles, or property. Unlike operating expenses, capital expenses cannot be fully deducted in the year you incur them. Instead, they are depreciated or amortized over the life of the asset.
Depreciation is a way for you to deduct a part of the cost of an asset each year. This way, the expense is spread out over multiple years, which mirrors how the asset is used to generate income. Knowing how to depreciate assets correctly can have a big effect on how much you save on taxes.
Here’s an example. If you buy a new computer for your business, you can’t deduct the entire cost in the year you bought it. Instead, you’ll spread out the cost over a number of years, based on how long the IRS says the asset will be useful.
Travel and Meals for Business
Understanding what is and isn’t deductible for business travel and meals is crucial. The IRS allows you to deduct travel expenses that are directly tied to your business activities. This includes things like transportation, lodging, and meals. But it’s important to remember that these expenses must be necessary and not overly luxurious or extravagant.
Let’s say you go to a business conference in a different city. You can write off the cost of your flight, hotel, and meals while you’re there. It’s a good idea to keep all your receipts and documentation, like conference schedules or itineraries, to prove the business nature of your trip.
Pay and Perks for Your Staff
One of the biggest expenses that can be deducted by small businesses is what you pay your employees. This includes not only their salaries or hourly wages but also any bonuses or commissions you might give them. Furthermore, if you offer benefits like retirement plans or health insurance, those can also be deducted. To explore more about maximizing these deductions, you can discover tax credits and hidden opportunities.
Imagine you own a small business with five employees. You pay them salaries, offer health insurance, and make contributions to a 401(k) plan. These are all deductible expenses that can substantially lower your business’s taxable income.
It’s important to make sure that the salary is fair and matches the industry standards. If the salary is too high, the IRS might investigate, so it’s a good idea to compare salaries with similar jobs in your industry. For further insights, consider exploring small business tax planning tips to ensure compliance and strategic financial management.
Advertising and Marketing Expenses
Advertising and marketing are essential for business growth, and fortunately, these expenses are typically deductible. Whether you’re sponsoring local events, printing flyers, or running online ads, you can deduct these costs as long as they’re directly related to your business promotion.
Remember, promotional costs must be for real business reasons. For instance, you might be able to deduct gifts for prospective clients, but there are restrictions on the amount you can claim. It’s critical to keep a close eye on these costs and retain all relevant paperwork. For more insights, explore our guide on business tax codes.
How to Track Expenses Accurately
- Automate your expense tracking with accounting software.
- Keep detailed and organized records of all transactions.
- Regularly review your expenses to make sure they are categorized correctly.
- Reconcile your bank statements every month to catch any discrepancies.
It’s crucial to track your expenses accurately to maximize your deductions and comply with tax laws. By keeping detailed records, you can easily figure out which expenses are deductible and have the necessary documentation if you’re audited.
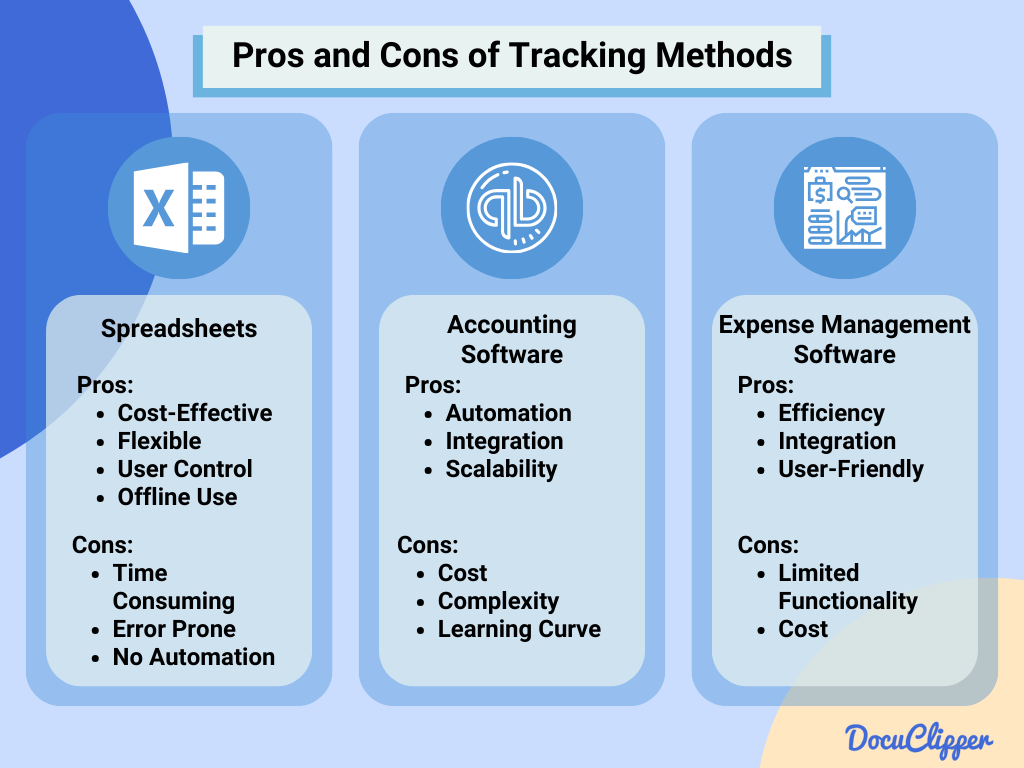
Using accounting software is one of the best methods for monitoring expenses. These tools can automate much of the process by categorizing expenses and creating reports that help you understand your financial situation.
In addition to using software, it’s important to keep detailed and organized records. This means saving all receipts, invoices, and other important documents. Think about creating a filing system, either digital or physical, to store these records in an efficient way.
Leveraging Accounting Software
Accounting software can be a godsend for small business owners. It makes it easier to keep track of expenses, create financial reports, and get ready for tax season. Well-known choices like QuickBooks, Xero, and FreshBooks have features designed for small businesses, making it a breeze to classify expenses and keep your finances in check.
Why You Should Keep Detailed and Organized Records
Keeping detailed and organized records isn’t just a good idea—it’s a must. Detailed records back up your deductions and give you a clear idea of your financial health. Make it a point to record every transaction, whether it’s a small office supply purchase or a large equipment investment.
Keeping Track of All Business Expenses
Every penny counts when it comes to deductions. Be sure to keep track of every expense, no matter how small. This includes keeping receipts, invoices, and bank statements. For digital transactions, save electronic receipts and emails confirming purchases. Keeping a thorough record not only helps with deductions but also protects you in case of an audit.
Getting Professional Advice
Figuring out tax deductions can be a daunting task. That’s when getting professional advice can really help. Hiring an accountant or a tax consultant can give you the information you need and make sure you’re getting all the deductions you’re entitled to while still following the tax laws.
Working with an Accountant
Having an accountant on your team can be a game-changer for your business. They can guide you through the maze of tax deductions, make sure your books are up to date, and offer strategic financial counsel. By capitalizing on their skills, you can concentrate on managing your business while they take care of the financial specifics.
Why You Should Consult a Tax Professional
Tax professionals are experts in the constantly evolving world of tax laws and regulations. They can help you find deductions you might have overlooked and make sure your tax return is accurate and thorough. Consulting a tax professional can save you time, lessen stress, and possibly increase your tax savings. For more insights, check out these small business tax planning tips.
In addition, tax professionals can provide strategic guidance on how to structure your business in a way that maximizes deductions and minimizes tax liability. Their advice can be especially useful in complex tax situations or when major changes happen in your business.
Taking Advantage of IRS Tools and Guides
Small business owners can benefit greatly from the array of tools and guides provided by the IRS. These include IRS Publication 535, which offers an in-depth look at business expenses and can be a useful tool for reference. By using these tools, you can deepen your knowledge and make sure you’re following all tax laws.
Conclusion: How to Get the Most Out of Your Business Expense Deductions
In conclusion, knowing what small business expenses are deductible and claiming them is a great way to reduce your taxable income and improve your business’s financial health. By knowing what types of expenses are deductible, keeping good records, and getting professional advice, you can make sure you’re getting the most out of your deductions and staying on the right side of the tax laws.

Keep in mind, each dollar you save on taxes is a dollar you can put back into your business. By being mindful and keeping accurate records, you can maximize your deductible expenses and set your business up for lasting success.
How to Stay Compliant
It’s critical for small business owners to stay compliant with tax laws. A crucial step in this process is keeping precise and thorough records of all business transactions. This includes hanging onto receipts, invoices, and any other documents that back up your deductions. Frequently checking and balancing your accounts can help you spot inconsistencies early on and avoid potential problems with the IRS.
It’s also important to stay up-to-date on changes in tax laws and regulations. Tax laws often change, and knowing about these changes can help you take all the deductions you’re entitled to and stay on the right side of the law. Talking to a tax professional can give you useful information and help you deal with complicated tax issues.
The Long-Term Advantages of Correct Expense Management
Correct expense management provides several long-term advantages for your company. By precisely monitoring and categorizing expenses, you get a clearer picture of your financial situation. This knowledge enables you to make educated decisions, effectively distribute resources, and plan for future expansion.
In addition, good expense management can improve your business’s trustworthiness and reputation. When potential investors or lenders see that you are in control of your finances, they are more likely to trust your business and think about investing or lending money. This can lead to new opportunities and help your business succeed in the long run. For more insights, explore our small business tax planning tips.
Common Questions
Many small business owners wonder about deductible expenses and how to get the most tax savings. Here are some common questions and answers to help you understand this important part of business finance.
How can a small business determine if an expense is deductible?
If an expense is both ordinary and necessary for your business, it is deductible. An ordinary expense is one that is generally accepted in your industry, and a necessary expense is one that is helpful and appropriate for your business operations. The IRS provides guidelines to help determine if an expense is deductible.
How do I separate my personal expenses from my business expenses?
It’s crucial to keep your personal and business finances separate in order to distinguish between personal and business expenses. Only expenses that are directly related to the operation of your business can be claimed as deductions. If an expense has both a personal and a business component, only the business portion can be deducted. Keeping detailed records and notes can help clarify the purpose of each expense.
Can small businesses deduct depreciation?
Absolutely, small businesses can deduct depreciation. Depreciation gives you the ability to deduct the cost of an asset over its lifespan, which accounts for its gradual wear and tear. This deduction can be claimed each year and it helps to lower your taxable income. It’s crucial to adhere to the IRS rules on how to figure out and report depreciation for various kinds of assets.
Take, for instance, when you buy a machine for your company, you can depreciate its cost over a few years, spreading the deduction over the machine’s useful life. This gives a consistent tax benefit over time. For more insights on maximizing your business benefits, explore these small business tax credits tips and strategies.
Can I deduct my startup costs?
Yes, you can deduct your startup costs, but there are certain rules you must follow. The IRS lets you deduct up to $5,000 in startup costs in the year your business starts. Any costs that are left over can be spread out over 15 years. Startup costs include any expenses that are involved in starting your business, like legal fees, market research, and advertising.
Keep in mind that only expenses that occur before your business is up and running are classified as startup costs. Once your business is in operation, these costs are considered to be regular business expenses.
What’s the best way to manage home office expenses?
If you’re using part of your home for business purposes on a regular and exclusive basis, you can deduct your home office expenses. The IRS provides a simplified way to calculate this deduction, which allows you to deduct $5 per square foot of your home office space, with a limit of 300 square feet.
Or, you can figure out the deduction by looking at the actual expenses you had, like part of your mortgage or rent, utilities, and insurance. It’s important to keep good records and paperwork to back up your home office deduction.
For example, if you have a specific room in your house that you only use for your business, you can calculate the square footage and use the simplified method to take the deduction. This method makes the process easier and guarantees that you’re getting the most out of your deduction.
Are business insurance costs deductible?
Indeed, business insurance premiums are usually deductible. This encompasses insurance policies that safeguard your business assets, liability insurance, and employee health insurance plans. Deducting these expenses can substantially lessen your taxable income and offer financial protection for your business.
What are some non-deductible expenses?
Not every expense can be deducted. A few common examples of non-deductible expenses are personal expenses, fines and penalties, and political contributions. Some entertainment expenses also may not be deductible unless they meet certain IRS criteria. Knowing these limitations is crucial to avoid claiming non-deductible expenses on your tax return.
For example, you can deduct the cost of a meal with a client, but you might not be able to deduct the cost of taking a client to a sports event. The IRS has specific rules for when entertainment expenses can be deducted.
How frequently should I check my deductible expenses?
Regularly checking your deductible expenses, preferably every month, is a good habit to develop. This allows you to keep track of your finances, spot any mistakes or inconsistencies early, and make sure your records are current. Regular checks also help you spot patterns and make educated choices about your business’s financial strategy.
By being proactive and organized, you can ensure that you save as much as possible on your taxes and that you are following tax laws. Regular reviews also provide a chance to check on your business’s financial health and make any necessary changes to support growth and success. For more insights, consider exploring small business tax planning and financial analysis tools.

