Important Points
- The General Data Protection Regulation, or GDPR, is an EU law that protects personal data.
- If a small business processes the data of EU citizens, it must comply with GDPR, even if it’s not based in the EU.
- Fines for non-compliance can be severe, reaching up to €20 million or 4% of global turnover, whichever is higher.
- The main principles of GDPR are lawfulness, fairness, transparency, data minimization, and integrity.
- Steps towards compliance include data mapping, developing a privacy policy, managing cookies, and handling data requests.
The Importance of GDPR for Small Businesses
The General Data Protection Regulation, or GDPR, is crucial for any business that deals with the personal data of EU citizens. Even if your business is not in the EU, you still need to follow the rules if you process data from EU residents. This regulation is about protecting individuals’ data and giving them more say in how it’s used.
First and foremost, failing to comply can result in harsh punishments. These can be fines as high as €20 million or 4% of your worldwide revenue, whichever is greater. As a result, it is critical for your company’s survival and reputation to understand and implement GDPR.
In addition, GDPR compliance can help you establish trust with your clients. They will feel more secure knowing that their information is being treated with respect, which can result in improved customer relationships and loyalty.
Getting to Know the Fundamentals of GDPR
So, what is GDPR? It’s an acronym for General Data Protection Regulation, a law enacted by the European Union. Its primary purpose is to safeguard personal data and guarantee privacy for individuals living in the EU. For small businesses, following a GDPR compliance guide can be crucial to ensure all regulations are met.
Personal data refers to any information that can be used to identify an individual, such as their name, email, address, or even their IP address. The GDPR applies to both data controllers, who determine how and why personal data is processed, and data processors, who process the data on behalf of the controller. For small business owners, understanding these roles is crucial for compliance with employment laws.
The GDPR is built on several fundamental principles, and understanding them is crucial for businesses. For a detailed checklist, refer to this Small Business GDPR Compliance Guide.
- Legality, Fairness, and Transparency: Data must be processed in a way that is lawful, fair, and transparent.
- Limitation of Purpose: Data must be collected for specific, explicit, and legitimate purposes.
- Data Minimization: Only collect data that is necessary for the intended purpose.
- Accuracy: Ensure data is accurate and kept up to date.
- Limitation of Storage: Do not keep data longer than necessary.
- Integrity and Confidentiality: Ensure data is secure and protected against unauthorized access.
- Accountability: Be able to demonstrate compliance with these principles.
Determining the Scope of GDPR for Your Business
The first step is to understand if GDPR applies to your business. If you offer goods or services to EU citizens or monitor their behavior, you need to comply with GDPR, regardless of where you are located.
Who Is Required to Comply?
Small businesses sometimes believe they’re exempt from GDPR, but that’s incorrect. If your company has any customers or clients in the EU, or if your website gathers data from EU residents, you’re required to comply. This includes businesses such as online retailers, service providers, and even bloggers who gather email addresses. For more strategies, check out these small business expansion tips.
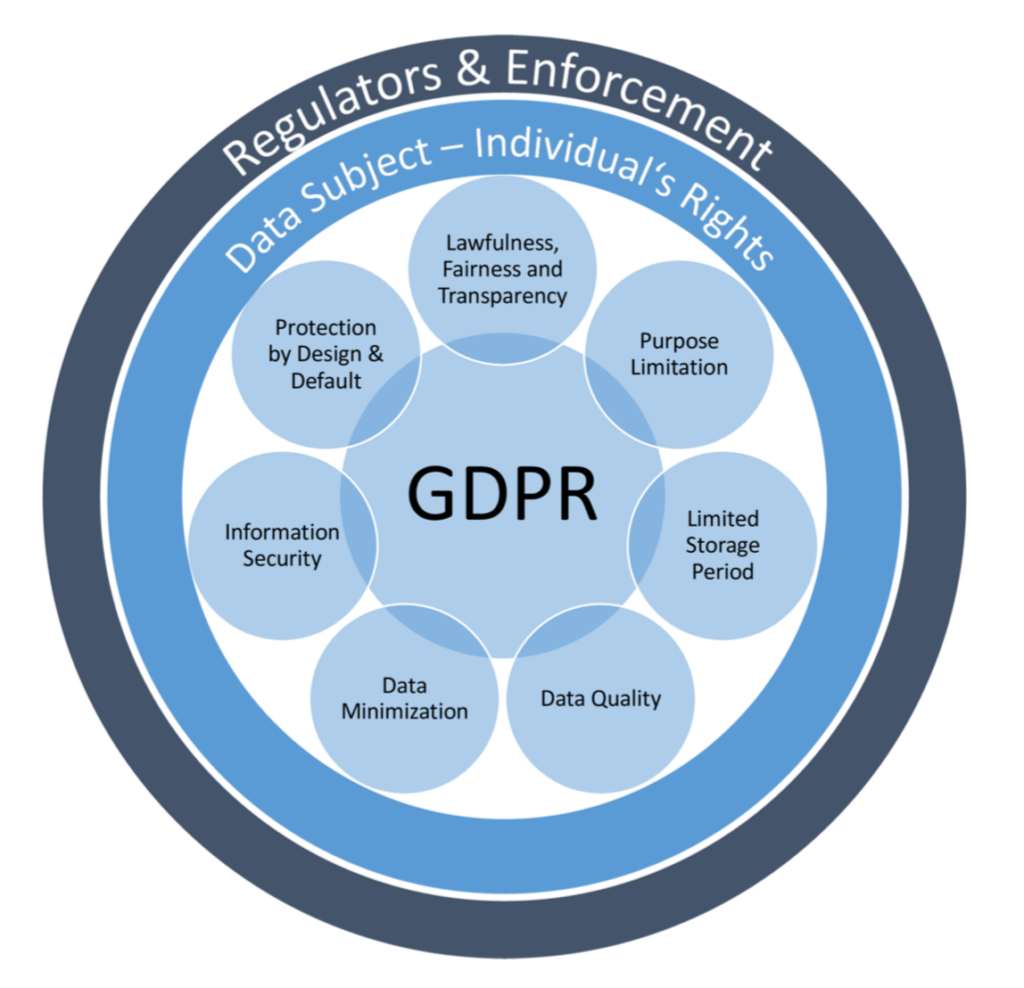
Key Principles of Data Protection
Let’s take a closer look at the main principles of GDPR:
- Legality, fairness, and transparency: You must have a legitimate reason to collect data, such as the individual’s consent, and you must be transparent about how their data will be used.
- Limitation of purpose: Only use data for the purpose it was collected for. For instance, if you collected an email for a newsletter, don’t use it to market other products without consent.
- Minimization of data: Only collect the data you need. If you don’t need someone’s phone number, don’t request it.
- Accuracy: Ensure the data you have is accurate. Allow users to update their information if necessary.
- Limitation of storage: Don’t retain data longer than necessary. If you no longer need it, erase it.
- Integrity and confidentiality: Protect data from unauthorized access or breaches. Use encryption and secure storage solutions.
- Accountability: Be capable of demonstrating that you comply with GDPR. Keep records of your data processing activities.
Penalties of Non-Compliance
Ignoring GDPR can be expensive. Fines can reach up to €20 million or 4% of your annual global turnover, whichever is higher. But the damage extends beyond fines. Your business reputation can suffer, leading to loss of customers and trust.
Apart from monetary fines, you may also be subject to lawsuits from people whose data rights have been infringed. As such, GDPR compliance isn’t just about dodging penalties; it’s about protecting your business and its future.
How to Comply with GDPR
Mapping and Documenting Data
The first thing you need to do to comply with GDPR is to understand the data you collect and what you do with it. This is known as data mapping. Make a comprehensive record of all the personal data you deal with, including where it comes from, where you keep it, and who can access it. For more tips on data management, you can explore effective strategies for managing remote teams.
It is vital to record this data. It allows you to spot any possible hazards and guarantees you can prove compliance if necessary. Utilize a basic spreadsheet to monitor all your data processing tasks.
Developing a Privacy Policy that Adheres to GDPR
Your privacy policy is a crucial element in adhering to GDPR. It needs to plainly state what data you gather, the reasons you gather it, how you utilize it, and how individuals can use their data rights.
Ensure your privacy policy is user-friendly. Skip the legal terms and opt for layman’s language. Put it somewhere noticeable on your website, and ensure users can readily find it before they give any personal information.
Developing a Privacy Policy in Line with GDPR
To ensure your privacy policy aligns with GDPR, it needs to address several important points. Begin by detailing the personal data you gather and the reason for its collection. For instance, you may gather email addresses for newsletter distribution or names and addresses for product shipment.
Then, talk about the way you keep and safeguard this data. Point out any security measures you have implemented, like encryption or secure servers. Additionally, detail how long the data will be kept and when it will be removed.
Lastly, make sure to let your users know about the rights they have under GDPR. They can access their data, correct any mistakes, ask for their data to be deleted, and object to certain ways their data is processed. Be sure to give them clear instructions on how to do this, like through a contact form or an email address. For more detailed information, you can refer to this small business GDPR compliance guide.
Understanding Cookie Policies and Managing Consent
Cookies are tiny files that are stored on a user’s device and are used to track their activity on your website. According to the GDPR, you need to get explicit consent before using cookies that gather personal data. This means you cannot use pre-ticked boxes or implied consent.
Make sure to include a cookie consent banner on your website that pops up when someone first visits. This banner needs to explain in clear terms what cookies are, what kind of information they gather, and how that information will be utilized. Visitors should be able to choose whether or not they want to accept non-essential cookies. For more information on compliance, check out our small business insurance guide.
Agreements for Processing Data (DPAs)
When you have third parties that process personal data for you, it’s crucial to have Agreements for Processing Data (DPAs) in place. These agreements detail the responsibilities of each party and make sure that the third party is also in compliance with GDPR.
Data Protection Agreements should include a variety of important topics, such as the nature and purpose of the processing, the types of personal data involved, and the security measures in place. Regularly review and update these agreements as necessary to ensure compliance with employment law.
Requests for Personal Data Access
The GDPR gives individuals the right to access their personal data that you have on file. This is called a Request for Personal Data Access. You have one month to respond to these requests and must provide the data in a format that is easy to understand. For more information on compliance, you can read about nonprofit payroll compliance.
Establish a protocol for dealing with DSARs. Appoint an individual or group to oversee these inquiries, and develop a regular method for confirming the requester’s identity and collecting the necessary data. For more information on maintaining compliance, you can refer to our nonprofit payroll compliance guide.
How to Stay Compliant with GDPR: Handy Tips
- Regularly audit your data to maintain compliance.
- Ensure your employees are trained on GDPR rules and best practices.
- Put in place robust security measures to safeguard personal data.
- Stay current with any changes to GDPR regulations.
- Utilize tools and resources that can make compliance tasks easier.
Staying compliant with GDPR is a continuous process. It’s crucial to regularly audit your data to ensure you’re still meeting GDPR requirements. These audits should include a review of all data processing activities, identification of any potential risks, and the implementation of any necessary corrective actions. For more tips on managing your small business, check out this guide on effective small business management strategies.
It’s also important to educate your employees. Make sure all team members are aware of GDPR and what it means for their roles. Regular training sessions and updates will help keep everyone in the loop about any changes to the regulation. For a comprehensive guide, refer to our small business GDPR compliance checklist.
In addition, it’s crucial to have robust security measures in place to protect personal data. Utilize encryption, secure servers, and frequent security assessments to keep your data safe from breaches and unauthorized access.
Training and Awareness Among Staff
One of the most crucial steps in staying compliant with GDPR is training your staff. Every member of your team should have a basic understanding of GDPR, know their role in safeguarding personal data, and be aware of how to handle data securely.
Conduct ongoing training sessions for both new and current employees. Use real-world scenarios and case studies to highlight the significance of GDPR and the possible outcomes of non-compliance.
Consistent Data Reviews and Checks
By performing consistent data reviews, you can ensure that you’re meeting your GDPR requirements. These reviews should cover everything related to your data processing activities, including how you collect, store, and share data.
Spot any possible threats or non-compliance areas and fix them quickly. Keep a record of your audits and any actions taken to fix problems. This can show that you are committed to GDPR compliance.
Handling Incidents and Responding to Breaches
Despite having top-notch security measures, data breaches may still occur. It’s crucial to have a solid plan for managing incidents and responding to breaches in order to reduce the damage of a breach and maintain compliance with GDPR.
Your strategy should delineate the actions to be taken if a breach occurs, including how to detect and limit the breach, evaluate the consequences, and inform impacted individuals and regulatory bodies. Ensure that all staff members are aware of the strategy and their responsibilities in the event of a breach.
Utilizing GDPR Compliance Tools and Resources
Several tools and resources are available to aid small businesses in achieving and maintaining GDPR compliance. These include data mapping tools, consent management platforms, and GDPR compliance software.
By leveraging these tools, you can effortlessly manage your data protection responsibilities and keep abreast of any changes in GDPR regulations. Opt for tools that provide features such as automated data mapping, consent tracking, and breach reporting to make your compliance efforts more efficient.
GDPR Compliance in Action: Real Business Examples
We’ll explore some actual examples of small businesses that have effectively achieved GDPR compliance. Studying these instances can offer helpful perspectives and takeaways that you can use in your own company.
Case Study: Small E-commerce Business
A small e-commerce business that sells handmade crafts online needed to comply with GDPR because they had customers in the EU. They started by conducting a data audit to identify all the personal data they collected, including customer names, addresses, and payment information.
They then updated their privacy policy to clearly outline how this data was used and put a cookie consent banner on their website. They also established a process for managing DSARs and educated their staff on GDPR regulations.
After following these steps, the company not only achieved GDPR compliance but also gained the trust of their customers, which led to increased sales and customer loyalty.
Case Study: Digital Marketing Agency
A digital marketing agency that provided online services was required to adhere to GDPR as they handled personal data from clients in the EU. They began by outlining all their data processing activities and pinpointing any third parties they shared data with.
They then established Data Protection Agreements with all their third-party processors and updated their privacy policy to reflect their data practices. They also put a solid data breach response plan in place and conducted regular training sessions for their employees.
Therefore, the service provider managed to comply with GDPR and show their dedication to data protection, which enabled them to draw in more customers and expand their business by implementing top local SEO strategies.
Real-life Example: Digital Marketing Agency
A digital marketing agency that provided services online had to become GDPR compliant because they were handling personal data from customers in the EU. They began by outlining all of their data processing activities and pinpointing any third parties they were sharing data with. For a comprehensive guide, refer to this small business GDPR compliance guide.
They subsequently established DPAs with every one of their third-party processors and modified their privacy policy to reflect their data practices. They also put a solid data breach response plan in place and held frequent training sessions for their employees. For more details on GDPR compliance, you can refer to this GDPR compliance guide.
Therefore, the service provider managed to become GDPR compliant and show their dedication to data protection, which allowed them to draw in more customers and expand their business.
Insights and Recommended Strategies
These case studies offer us important insights and recommended strategies for achieving GDPR compliance:
- Carry out a comprehensive data audit: Familiarize yourself with the data you collect, how it’s utilized, and where it’s stored.
- Revise your privacy policy: Provide a clear explanation of your data practices and make it easily accessible to users.
- Set up consent management: Employ cookie banners and secure explicit consent for data collection.
- Utilize Data Processing Agreements: Guarantee that third-party processors also adhere to GDPR.
- Educate your employees: Regular training sessions assist staff in understanding their obligations under GDPR.
- Be ready for data breaches: Have a well-defined incident management and breach response plan ready.
Commonly Asked Questions (FAQ)
To assist you in better understanding GDPR compliance, here are responses to some commonly asked questions:
What does GDPR stand for and why was it created?
The GDPR, which stands for General Data Protection Regulation, is a law that was passed by the European Union. Its purpose is to protect the personal data of those who live in the EU. It was created to give people more power over their own data, and to make sure that businesses are handling personal data in a responsible and transparent way.
Does GDPR affect businesses located outside of the EU?
Indeed, GDPR affects any business that handles the personal data of EU citizens, no matter where the business is located. This implies that even if your business is located outside of the EU, you still need to adhere to GDPR if you process data from EU residents.
What does GDPR consider personal data?
Personal data under GDPR is any information that can be used to identify a person, directly or indirectly. This includes things like names, email addresses, phone numbers, IP addresses, and even cookie identifiers. In other words, if the data can be used to identify a person, it falls under the category of personal data.
What are the consequences of not complying with GDPR?
Not complying with GDPR can have serious consequences. You could be fined up to €20 million or 4% of your company’s annual global turnover, whichever is greater. Besides the financial penalties, not complying can harm your business’s reputation and result in legal action from individuals whose data rights have been violated.
How can small businesses handle the cost of GDPR compliance?
Even though GDPR compliance might seem like a hefty expense, there are strategies to handle the costs. You can start by carrying out a data audit and updating your privacy policy, which are relatively inexpensive measures. Make use of free or low-cost GDPR compliance tools and resources, and think about hiring outside experts for certain tasks if necessary. Keep in mind, the cost of not complying can be much greater than the cost of complying.
Can I use tools to help me comply with GDPR?
Definitely, there are a host of tools out there designed to help small businesses reach and maintain GDPR compliance. These range from data mapping tools to consent management platforms to GDPR compliance software. Some of the more popular tools include OneTrust, TrustArc, and Termly. These tools can make managing your data protection obligations a breeze and ensure you stay on top of any changes in GDPR regulations.
How frequently should we check our GDPR compliance status?
It’s crucial to check your GDPR compliance status on a regular basis. You should perform data audits at least annually, and revise your privacy policy and data processing agreements as necessary. You should also regularly train your staff on GDPR requirements and best practices, and keep up to date on any changes in GDPR regulations. By regularly reviewing and updating your compliance efforts, you can make sure that your business stays compliant and avoids possible fines.
By adhering to these guidelines and best practices, small businesses can achieve and maintain GDPR compliance, safeguarding both their customers’ data and their own business interests. It’s important to remember that GDPR compliance is not a one-off task but a continuous commitment to data protection and privacy.
The content you provided is empty. Please provide the content you want to be rewritten.

